Business that manufacture electronics or electronic components know how important it is to protect this sensitive technology from environmental damage. That’s where encapsulation and potting solutions come in. Today’s post will discuss the purpose of potting electronic components, what’s typically involved in this process, and how your own business may be able to improve your existing dispensing solutions.
What is the Purpose of Potting or Encapsulation?
Although potting and encapsulation are slightly different, they essentially serve the same purpose. These processes, which involve filling an electronic assembly with epoxy or other types of compounds, are meant to protect these components from moisture, corrosion, and vibration. Because electronic elements are quite delicate, they can easily be damaged by the environment in which they’re kept. Dust, debris, water, extreme temperatures, and other conditions can cause harm unless the electronic components are properly protected with potting solutions.
What is Involved in the Potting Process?
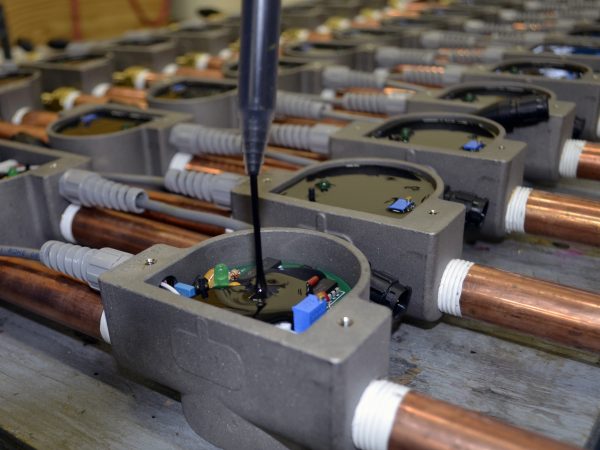
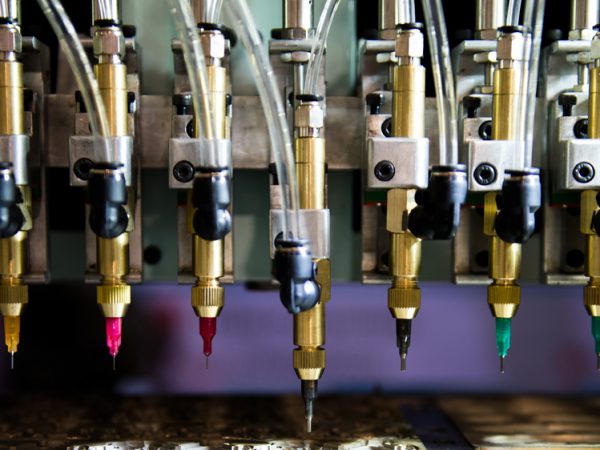
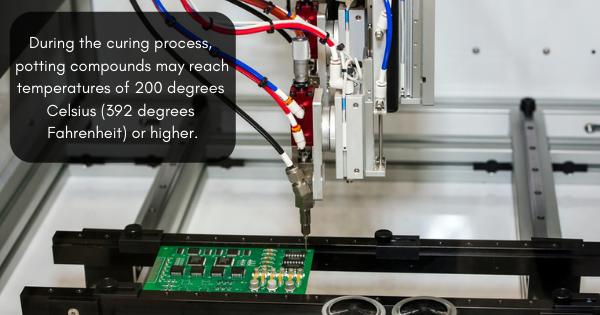
While encapsulation typically refers to dipping a device into a resin or other fluid to completely coat the unit, potting usually involves placing a device into a mold or case and then pouring the liquid compound over the top to completely cover it. With potting solutions, the case or mold will typically stay part of the finished unit. After the potting design is mapped out and the proper solution is selected, the mold can be made. Then, the electronics are encased in the potting solutions or compounds.
After that, the potting compound will need to cure. Curing refers to the amount of time it takes for the potting compound to reach its fully functional state (or to harden), which depends on the type of material being used. During the curing process, potting compounds may reach temperatures of 200 degrees Celsius (392 degrees Fahrenheit) or higher. Temperature cycling is often used to determine whether the potting compound is completely cured. If the performance of the compound is unaffected after these cycling tests, the compound can be considered suitable and the potting process can be considered a success. In other words, it can withstand extreme conditions and adequately protect the components inside from damage.
How Can Businesses Improve Their Potting and Encapsulation?
If you feel that your current potting or encapsulation processes are inefficient or produce inconsistent results, you may need to take a closer look at the equipment and at the compounds you’re using. It’s a good idea to discuss your needs with dispensing machine manufacturers and epoxy suppliers to ensure that you’re benefitting from the latest technology and from the compounds that will more adequately serve your needs. To learn more about our dispensing equipment and other related products, please contact us today.





